Lab 8 for ENSC 180
Code
function mse = dft_denoise(threshold)
% DFT denoising function
% Input:
% threshold - the denoising threshold
% Output:
% mse - Mean Squared Error
% Step 1: Reset RNG
rng('default');
% Step 2: Create clean signal
f1 = 1; f2 = 10; f3 = 20; % Frequencies in Hz
t = (0:255)/256; % Time vector
x0 = 3*sin(2*pi*f1*t) + cos(2*pi*f2*t) + 2*sin(2*pi*f3*t); % Clean signal
% Step 3: Create noisy signal
noise = randn(1, 256);
x_noisy = x0 + noise;
% Step 4: Plot clean and noisy signal
figHandle1 = figure; % Store figure handle for the first plot
fig1 = tiledlayout(3, 1);
nexttile;
plot(t, x0);
title('Clean Signal');
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Amplitude');
nexttile;
plot(t, x_noisy);
title('Noisy Signal');
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Amplitude');
% Step 5: Calculate DFT of the noisy signal
X = fft(x_noisy);
% Step 6: Compute magnitude of DFT
magnitude = abs(X);
% Step 7: Plot DFT magnitude
figure; % Creating a new figure without needing its handle since it's the last figure
fig2 = tiledlayout(2, 1);
nexttile;
plot((0:255) / 256, magnitude);
title('Magnitude of DFT (Noisy Signal)');
xlabel('Frequency');
ylabel('Magnitude');
% Perform denoising
magnitude_denoised = magnitude;
magnitude_denoised(magnitude < threshold) = 0;
% Plot denoised DFT magnitude
nexttile;
plot((0:255) / 256, magnitude_denoised);
title('Magnitude of DFT (Denoised Signal)');
xlabel('Frequency');
ylabel('Magnitude');
% Step 10: Denoise complex DFT output
X_denoised = X;
X_denoised(abs(X) < threshold) = 0;
% Step 11: Inverse DFT to time domain
x_denoised = ifft(X_denoised);
% Step 12: Calculate MSE
mse = mean((x0 - x_denoised).^2);
disp(['Mean Squared Error: ', num2str(mse)]);
% Step 13: Plot denoised signal
figure(figHandle1); % Switch back to the first figure using its handle
nexttile;
plot(t, x_denoised);
title('Denoised Signal');
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Amplitude');
end
Input 150
>>mse = dft_denoise(150);- runs it with 150 threshold
Output 150
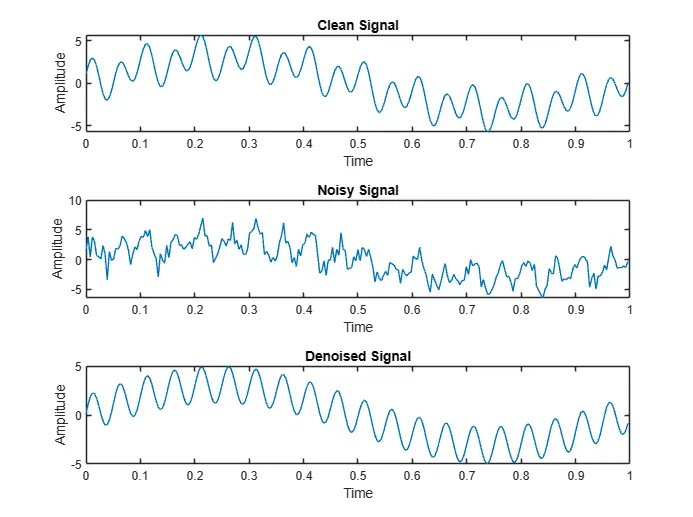
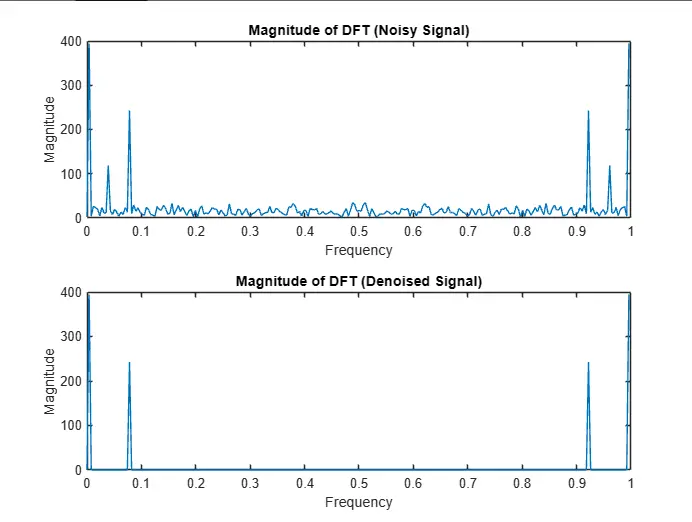
Mean Squared Error: 0.51732
Input 250
>>mse = dft_denoise(250);- runs with 250 threshold
Output 250
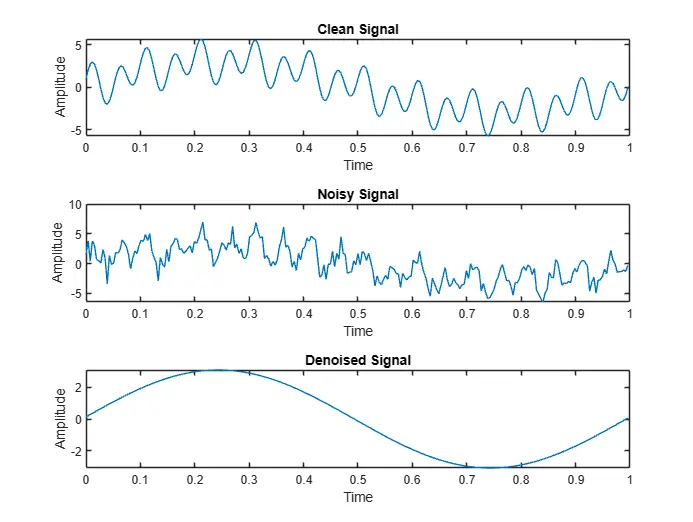
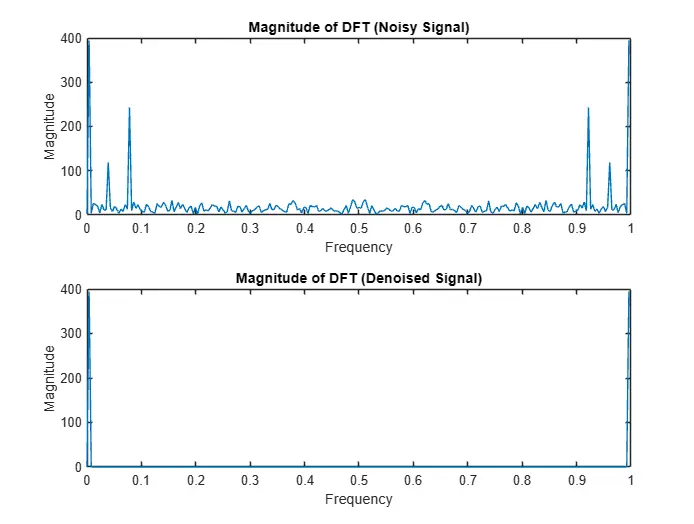
Mean Squared Error: 2.5119
Explanation
Observing DFT Magnitude for Optimal Threshold
- Optimal threshold reduces noise, preserves signal.
- Specific threshold not directly observed in simulation.
Results
- Noise added to clean signal for analysis.
- DFT computes signal’s frequency domain representation.
- Observing magnitude reveals noise and signal frequencies.
- Thresholding eliminates low magnitude DFT components.
- Threshold choice critical for effective denoising.
- MSE measures fidelity of denoised signal to original.
- Identical MSE suggests threshold impact non-differential.