11/15/2023 notes for ENSC 105W
Critical thinking
-
Bloom’s Taxonomy
- created by benjamin bloom
-
It is a hierarchy
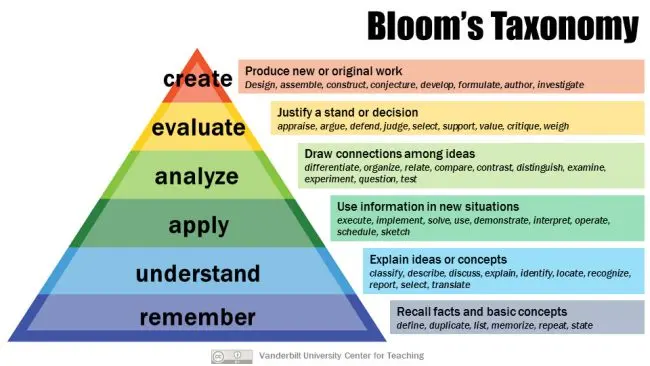
- as you move higher up the skills get harder
- persuasive paper is around evaluate
-
The cognitive domain
-
knowledge
-
Comprehension
-
application
-
analysis
-
synthesis
- put ideas together to form a whole
-
evaluation
-
Critical thinking and cognition
-
Critical thinking
- involve application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation
- the ability to ask questions
- answering questions is easy
- asking perceptive question is difficult
-
The effective Domain
-
Receiving phenomena:
- learners demonstrate awareness, willingness to hear
- selective attention
-
Responding to phenomena:
- participate actively by attending
- reacting to phenomenon
-
Valuing
- attching worth to a particular object
- phenomenon
- behavior
- ranging from simple acceptance
-
Organization
- organizing values into priorities by contrasting different values
-
Internalizing Values
- learners demonstrate a value system that controls their behavior in ways that are pervasive
-
The psycho-motor domain
-
Perception
- Learners demonstrate the ability to use sensory cues
-
Mind set
- Learners demonstrate a readiness to act
-
Guided response
- learners are at the early stages in learning a complex skill that includes initiation and trail and error
-
mechanism
-
adaption
-
Mental Models
-
Dualistic
- analyzes problems as black and white
-
Relativistic
- analyses the problem as shades of gray
-
Probabilistic
- analyzes problems based upon the balance of probabilities
-
Commitment
- analyzes problems based upon all of the above.
Recognizing and dealing with flaws
-
Pitfalls in persuasive papers
-
No persuasion:
- writing an informative paper instead of persuasive
-
Lost cause
- choosing a persuasive topic but failing to establish common ground
-
Straw man:
- arguing against a position that no reasonable, thinking person would hold
-
Bias:
- Overstating your case
- or using loaded language
- onsided arguments
-
Overstatement:
- making absolute statements
- if one exception happens then it would weaken your argument
-
No support
- lack of citations to provide support
-
Overwhelming
- using too many citations, where possible use your words to convince
-
Dichotomous thinking
- don’t have a binary system
-
Post Hocfallacy
