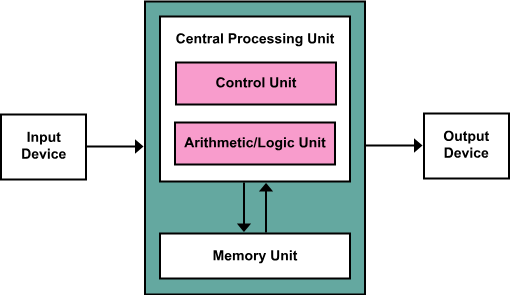
Common processor Architecture
-
Harvard
- optimized for speed
- program and data memories are contained in separate machines that can be accessed simultaneously
- typically deployed on simple processors
-
Von-neumann
- flexible design in which program and data share a common house
- not as efficient
- enables features not available in Harvard machines
- used in complex and most general purpose
- requires higher clock freq
Integrated circuit cost
dies per wafer* yeildcost per wafer
-
CPU exc time = cpu clock cycle x clock cycle time
-
CPU exec time = clockratecpu clock cycles
-
- reducing number of clock cycles
- increasing clock rate
- hardware designer must often trade off clock rate against cycle count
-
Clock cycels = instruction count x cycles per instruction (CPI)
-
CPU time = Instruction count x CPI x Clock cycle time
Clock Rateinstruction count x CPI
-
instruction counts
-
average cycles per instruction (CPI)
- determined by CPU hardware
- diff instructions have different CPI
- that’s why we are using the average value
-
Big picture
