Summary
-
3d Coordinate system and sketch:
- points
- surfaces
- curves
- regions
-
Geometry is a centerpiece of this course
- Sketching is a required skill and will be tested throughout this course
Review
-
Recall the 2D coordinate system
- We must be consistent in our graphs image
- We can rotate the graph
-
But we cant mirror it! (you could but you need to be consistent)
-
We can add a 3rd dimension by adding a line coming out of the intersection of the x-y plane
-
Right hand rule

- where we curve our hands towards the y-axis
-
Coordinates planes
-
We know the xy plane, but we can do this for all permutations of the varibles
-
X-Y Plane
-
X-Z Plane
-
Y-Z Plane
-
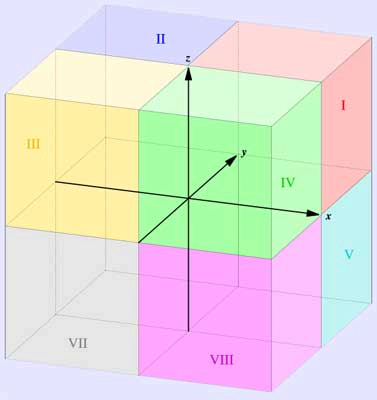
Because of this we have octants like the quadrants of a 2d plane
Coordinate systems in R3
-
It is simple it follows (x,y,z)
- this is self explanatory…
-
Projection of points to coordinate planes and axes.
-
If we are projecting onto a plane such as the xy plane we just take the xy coordinates and throwaway the rest
- this is similar to 1.5 Projection
- note we dont get rid of the redundant coordinate we just enter a 0
Sketching in R3
-
if its a 2 varible function we can just sketch it but we need to extrude in the direction of the free varible
-
Because the 3rd varible is a free varible so any value still would satisfy
-
EX.
-
The distance between two points P1(x,y,z) and P2(x,y,z) is
- ∣P1P2∣=(x1−x2)2+(y1−y2)2+(z1−z2)2
- this is derived because each point is perpidicular to each axis so they are sqares, we can just find the hypotunes